HTML Tables
The html-table component is still experimental and may be subject to change. Cross-check with the actual code in the codebase (e.g., zcl_abapgit_gui_page_codi_base and its subclasses).
General concept and features
- Create an instance of
zcl_abapgit_html_table - Define column structure with
define_column - Render the component, supplying the data and the renderer
- While rendering, the html table instance will call the appropriate renderer methods for each row and cell, yet hiding all routine table construction inside
Features
- styling individual cells and rows
- auto-marking columns with
column_iddata attribute - sorting support
Simplest table example
Suppose you have a table of this structure:
begin of ty_data,
id type i,
name type string,
city type string,
end of ty_data,Define the table structure:
column_idis the id to identify the column in further callbacks, in css styles, and also to be used as default field name to extract the value from a table record.column_titleis a visual name of the html table column.
li_table = zcl_abapgit_html_table=>create(
)->define_column(
iv_column_id = 'id'
iv_column_title = 'ID'
)->define_column(
iv_column_id = 'name'
iv_column_title = 'Name'
)->define_column(
iv_column_id = 'city'
iv_column_title = 'Location' ).Implement rendering methods render_cell and, optionally, get_row_attrs. This can be done directly in a calling component (typically), or in separate local classes (e.g. if there are several tables in the page).
method zif_abapgit_html_table~render_cell.
" This is the simplest form of rendering
" `iv_value` contains content of `column_id` field of table record
" `content` attribute of the returning structure
" is the text value to be rendered in the cell
rs_render-content = |{ iv_value }|.
endmethod.Finally, call the table render method to produce html. Pass the data table to be rendered and the renderer instance.
ri_html->add( li_table->render(
ii_renderer = me
it_data = value ty_data_tab(
( id = 1 name = 'John' city = 'London' )
( id = 2 name = 'Pierre' city = 'Paris' )
) ) ).
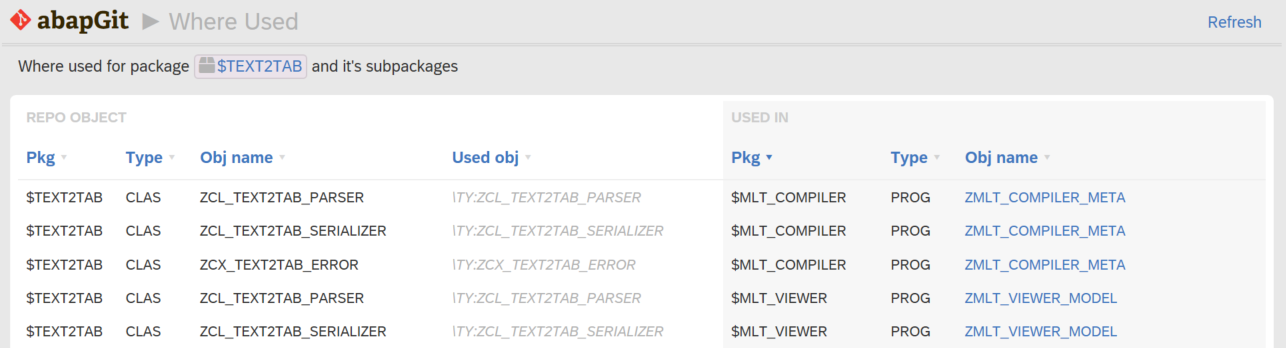
2-level header
You can create groups of columns with define_column_group. See an example in zcl_abapgit_gui_page_whereused class. title and id are both options, but you have to start before the first column if you plan to use groups (because it calculates spans from start).
CSS styles
There are several options to styling your table:
- First, you can pass the element id, and css class of the table itself to the
rendermethod. - Passing
iv_wrap_in_divparameter will wrap your table in anotherdivwith the given css class name, primarily for visual styling purposes (e.g. see padded borders and rounded corners in the screenshot below).
There are default CSS styles in abapGit to reuse if you don't want to bother with any specific styling - default-table and default-table-container, respectively, for the wrapping div.
ri_html->add( li_table->render(
iv_wrap_in_div = 'default-table-container'
iv_css_class = 'default-table'
iv_id = 'my-addr-tab'
it_data = ... ).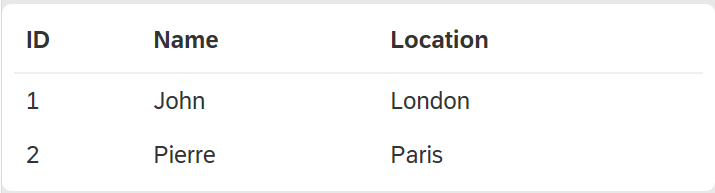
Rendering methods render_cell and get_row_attrs allow specifying css classes for individual cells and rows.
method zif_abapgit_html_table~get_row_attrs.
rs_attrs-css_class = 'my-tab-row'.
endmethod.
method zif_abapgit_html_table~render_cell.
" ...
rs_render-css_class = 'my-cell'.
endmethod.Finally, passing the iv_with_cids = abap_true param to render will auto-mark cells with data attribute data-cid with respecting column_id. This enables easy indirect CSS styling or reassembling memory representation of the table in Javascript.
ri_html->add( li_table->render(
iv_with_cids = abap_true
... ).get_row_attrs also allows passing a custom data attribute. Similarly, this can be used in CSS styling or JS.
method zif_abapgit_html_table~get_row_attrs.
rs_attrs-data-name = 'status'.
rs_attrs-data-value = 'error'.
endmethod.Resulting HTML:
<table id="my-addr-tab" class="default-table">
<thead>
<tr>
<th data-cid="id">ID</th>
<th data-cid="name">Name</th>
<th data-cid="city">Location</th>
</tr>
</thead>
<tbody>
<tr data-status="error">
<td data-cid="id">1</td>
<td data-cid="name">John</td>
<td data-cid="city">London</td>
</tr>
...
</tbody>
</table>CSS example:
table td[data-cid="id"] { font-weight: bold; }
table tr[data-kind="error"] { background-color: red; }If you use 2-level header and pass iv_group_id it will also appear as a data-gid attribute in all relevant cells.
Cell rendering
You can define your column so that the column_id and the field to take a value from have different names. In the example below the iv_value in render_cell will be taken from the person_id field in the table structure.
li_table->define_column(
iv_column_id = 'id'
iv_column_title = 'ID'
iv_from_field = 'person_id' ).You are not obliged to use iv_value in render_cell. Among the parameters of render_cell and get_row_attrs you will find also:
is_row- full table record being processed, to access the data flexibly and/or conditionallyiv_row_index- ... its indexiv_table_id- table id passed to therender(in case you want to render several tables with the same renderer instance. Though it is generally not the best practice, better avoid it and create separate local classes for each renderer)iv_column_id- column id of the current table column (forrender_cellonly)
Using the html attribute, you can return an instance of zif_abapgit_html. Use this if you want to return more complex HTML content.
method zif_abapgit_html_table~render_cell.
rs_render-html = zcl_abapgit_html=>create( )->add_a( ... ).
endmethod.Sorting
html_table component does not manage sorting over the data itself but rather provides helpers to visualize it and process appropriate events. The sorting itself should be done externally.
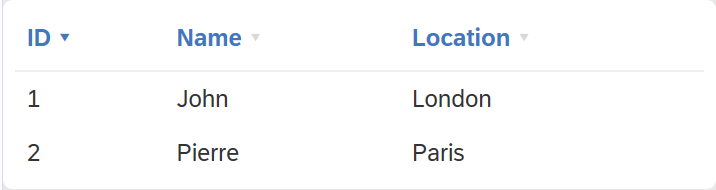
The sorting UI is triggered by passing is_sorting_state to the render. This is a structure consisting of two fields - column_id and descending value - which A) tells the component to visualize sorting B) tells which column is sorted and in which direction ( descending = true/false ).
In terms of CSS styles all sorting arrow are styled with sort-arrow class and the active one has additionally sort-active class. When designing an own CSS style, please don't create .sort-arrow names classes, but rather specify a more complete path table.my-tab th span.sort-arrow to avoid conflicts with the default-table style.
You can also pass iv_sortable = abap_false to define_column to remove the sorting possibility for a fiven column (by default all collumns are sortable).
Technical-wise sorting markers are links with events defined like sapevent:sort_by:id:dsc where id is a column id. This event must be properly processed in the host component. To simplify handling there is a helper method to identify and parse such an event. So the easiest way to handle sorting would be placing this code to the on_event:
data ls_sorting_request type zif_abapgit_html_table=>ty_sorting_state.
ls_sorting_request = zcl_abapgit_html_table=>detect_sorting_request( ii_event->mv_action ).
if ls_sorting_request is not initial.
ms_sorting_state = ls_sorting_request.
rs_handled-state = zcl_abapgit_gui=>c_event_state-re_render.
endif.... and then applying the ms_sorting_state elsewhere before rendering the table
In-table sorting
This feature is experimental, use with care. See zcl_abapgit_gui_page_whereused as an example.
To simplify sorting handling you may create your table component as a class member, and pass is_initial_sorting_state.
DATA ls_sorting_state TYPE zif_abapgit_html_table=>ty_sorting_state.
ls_sorting_state-column_id = 'xyz'.
mi_table = zcl_abapgit_html_table=>create(
is_initial_sorting_state = ls_sorting_state ).In the event handling method use process_sorting_request instead of detect_sorting_request.
IF mi_table->process_sorting_request( ii_event->mv_action ) = abap_true.
rs_handled-state = zcl_abapgit_gui=>c_event_state-re_render.
RETURN.
ENDIF.With this approach you will not need any other sorting logic to implement the table component will handle sorting for you. Please mind the caveats though:
- The
column_id(or suppliedfrom_field) must exist as a table field (for sortable columns) - To do the sorting the component creates a copy of the data internally. Mind memory consumption.